Fortress of Franzensfeste by Markus Scherer and Walter Dietl
Here are some photographs of a renovated fortress in northern Italy that now features patinated steel bridges, an extended underground tunnel and concrete towers.
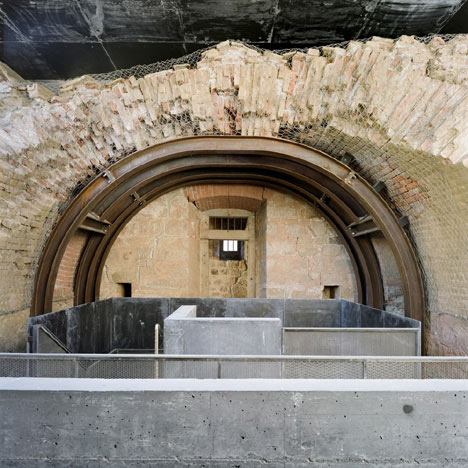

Austrian Italian architects Markus Scherer and Walter Dietl overhauled the site in 2009, when it hosted a regional exhibition.

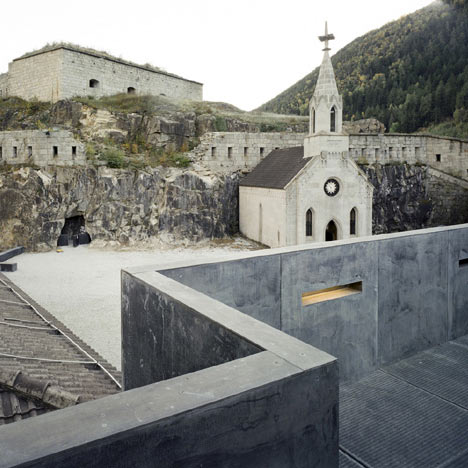
The fortified site was originally constructed in the nineteenth century by the Habsburg family, who were nervous about revolutionary iedas spreading from France and catching on in their own neighbourhood.

Since then, it has been used as a gunpowder depot, army territory and as a venue for the 2008 European contemporary art biennale.

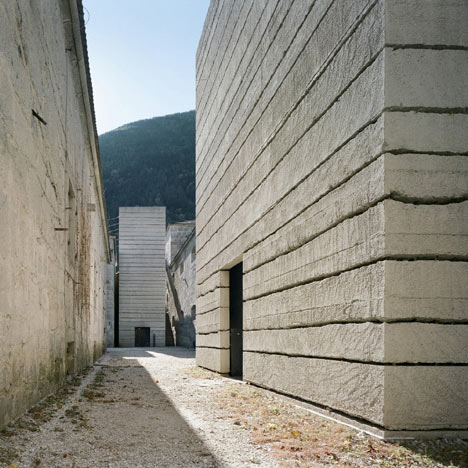
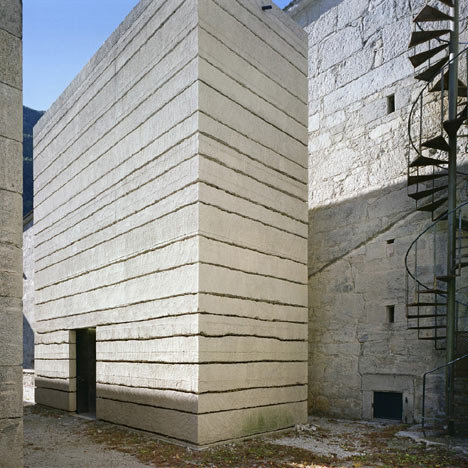
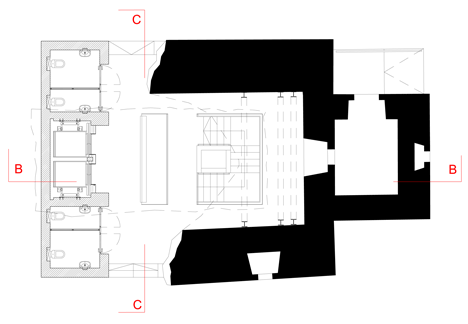
Two sandblasted concrete towers with horizontal fissures lead visitors through to a ticket office, shop, bar, restaurant and exhibition area.
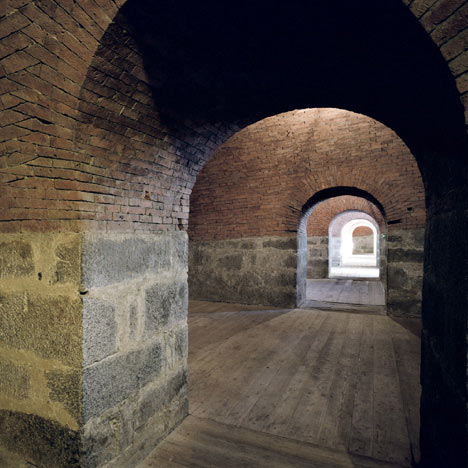

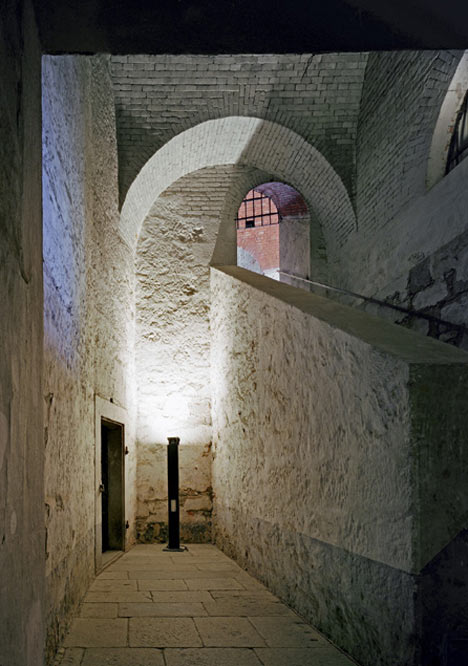
Restored vaults provide exhibition rooms with newly exposed brick arches and steel staircases.

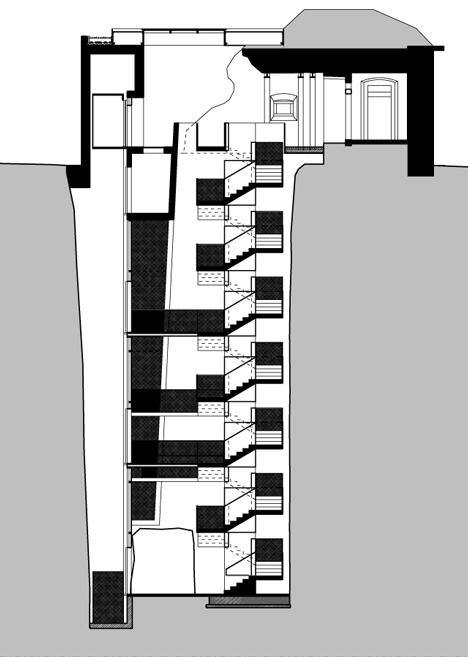
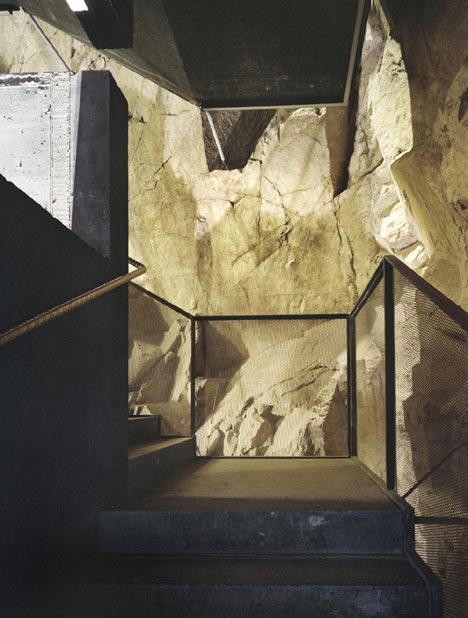
One of these staircases leads down into the extended underground tunnel, which was apparently once used to hide gold stolen from the Bank of Italy.

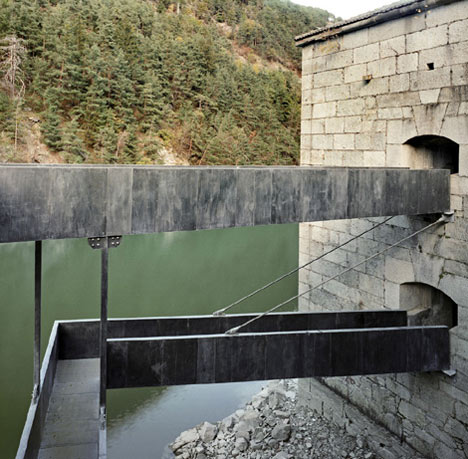
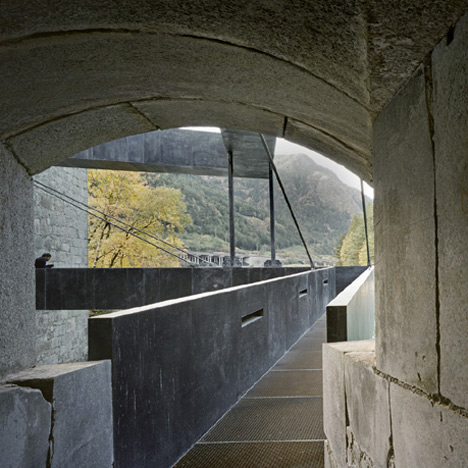
Steel bridges emerge from windows to create external routes between first and second floor rooms, crossing an artificial lake.

Elsewhere, the granite walls of all existing buildings onsite have been restored, while roofs have been waterproofed.

Other stories about renovated castles and strongholds include a castle converted into a mountain museum - see all our stories about castles here.

See also: our recent feature about about caves and grottoes.

Photography is by Alessandra Chemollo.
Here are some more details from Markus Scherer:
The Fortress of Franzensfeste
“Begun under Francis I in the year 1833 – completed by Ferdinand I in the year 1838”, reads the Latin inscription over the gate of the fortress. In just five years, over 6,000 workers and soldiers built a blocking position at one of the narrowest points in the Eisack valley. It has the dimensions of a small town and, with a surface area of 20 hectares, is the largest fortification in the Alpine region. With this monumental defensive work the Habsburgs hoped to halt the advance of the revolutionary changes provoked by the French revolution. Designed by regimental engineer Franz von Scholl, it consists of three autonomous sections: the upper, middle and lower fortress levels. It has clear and simple classicist lines; it is functional and impregnable. As the military threat did not materialise in the decades following its construction, however, the fortress rapidly lost its importance. By the end of the 19th century it was merely used as a powder depot. In 1918 Franzensfeste came under Italian rule and was used by the army until 2003.
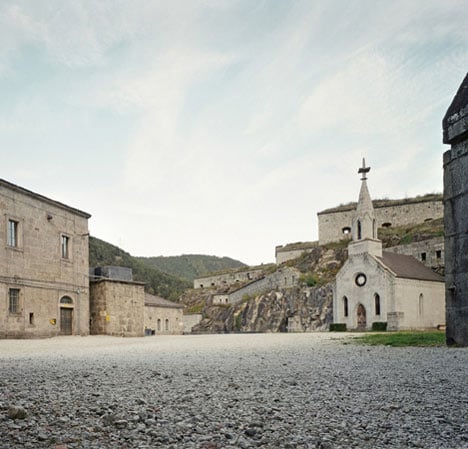

Acquired by the province of South Tyrol, new opportunities for the preservation of this cultural monument have arisen: the former fortress is intended to become a place for meetings and cultural exchanges. In 2008 it was one of the four venues for the European biennale of contemporary art, Manifesta 7, and in 2009 it hosted the South Tyrolean regional exhibition.

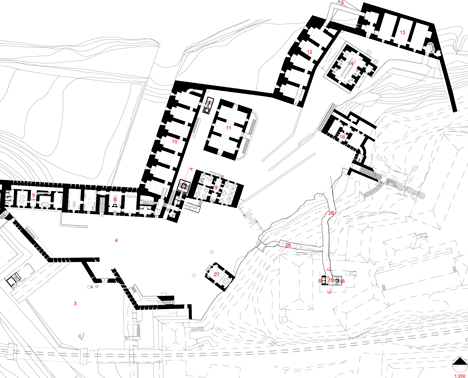
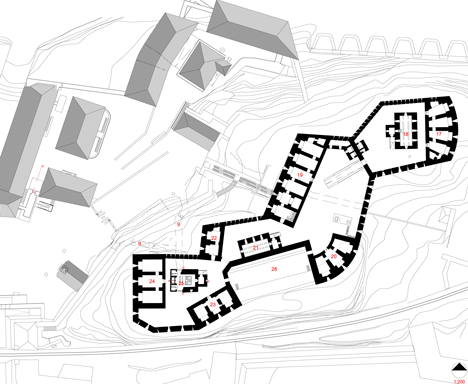
The Meran architect Markus Scherer prepared the lower fortress level for Manifesta 7, an exhibition surface area of over 3600 m². Preservation of the buildings and the character of the fortress was paramount. The huge granite blocks making up the walls were restored, the roofs waterproofed and the windows repaired. Walled-off spaces were opened up and later additions removed. The size and extent of the complex are not at first obvious from the courtyard behind the main gate. The monolithic structures with small, regularly spaced window apertures are on different levels around the compound, connected by ramps. The lowest are lapped by the dark waters of the adjacent artificial lake. New galvanised steel railings and staircases have improved safety. Two windowless concrete towers with lifts and staircases link the buildings. The surfaces and the material used interpret the historical building method anew: they are concreted in irregular 30-70 cm sections, with a fine layer of sand between each. These layers were flushed out to produce an irregular horizontal joint pattern and granite sand was used to adapt the towers to the surrounding colour, with the surface roughened by sandblasting.
Click above for larger image
These objects, with their military numbering, now accommodate a visitor centre with a ticket office and shop, as well as a bar, restaurant, a play area for children and, last but not least, a large exhibition area. Visitors to Manifesta are greeted by a seemingly endless series of rooms. The carefully restored vaults of exposed brick-work and the plastered walls, some decorated with murals, have retained the aura of the past. On one of the walls can be read “Immer vorwärts!”, always forwards, understandable in every language spoken in the Empire: let modern art breathe fresh life over the walls! New items such as grilles, handrails, doors and the two free-floating bridges over the lake, connecting two buildings, are all constructed of galvanised, patinated steel: the existing elements form a pleasant context for their cloudy black coloration.
Click above for larger image
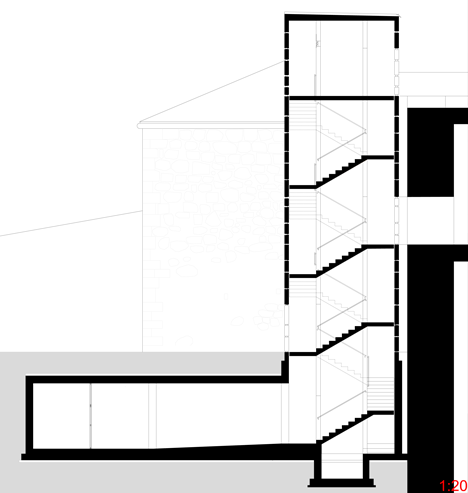
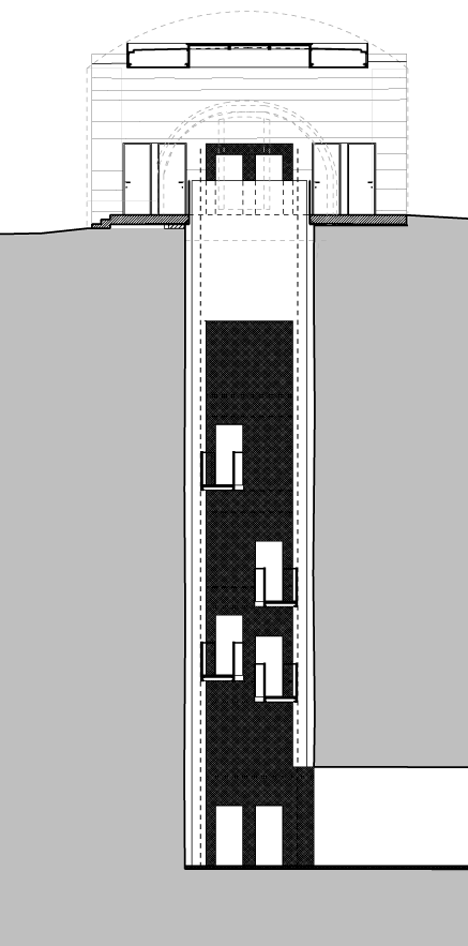
The existing tunnel, where the Bank of Italy’s stolen gold was found, was extended and a 22-metre long vertical shaft driven through the rock to connect the lower to the middle fortress. The black concrete stairway with its golden handrail (Kunst am Bau (The Art of Building) by Manfred Alois Mayr) spirals upwards like a sculpture.
Click above for larger image
The stairs and lift end in the partially destroyed powder magazine. This was redesigned as the new entrance building, while the new adjacent building of compressed concrete (coloured to match the existing construction through the use of granite sand) provides the outside edges of the missing sections and contains all the sanitary and technical areas for the middle fortress.
Click above for larger image
The remaining buildings have as far as possible been left as they were found. Only certain elements such as safety grilles, rails and ramps have been added and these, as in the lower fortress, are of galvanised, patinated steel.
Client: Autonome Provinz Bozen
Project managment: Arch. Josef March (main coordinator)
Geom. Hans Peter Santer (Project leader)
Hbpm Ingenieure - Ing. Julius Mühlögger, Ing. Gunnar Holzer (Project leader)
Architect: Markus Scherer, Meran with Walter Dietl, Schlanders
Construction supervisor: Markus Scherer, Meran – Klaus Plattner, Bozen
Collaborator: Heike Kirnbauer, Elena Mezzanotte
Structural engineering: Baubüro-Klaus Plattner, Bozen
Safety coordinator: Günther Rienzner, Bozen
Electrical and domestic engineering: Planconsulting, Burgstall
Finishing: 05.2009
Location: Festung Franzensfeste, Franzensfeste