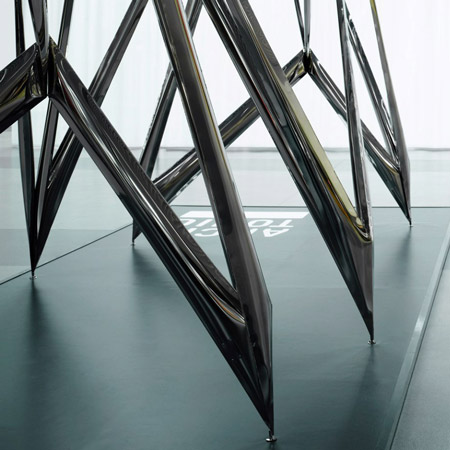

Architonic Concept Space III by Oskar Zieta
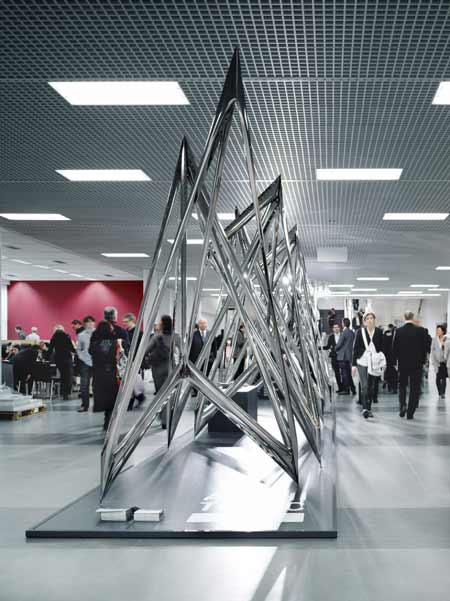
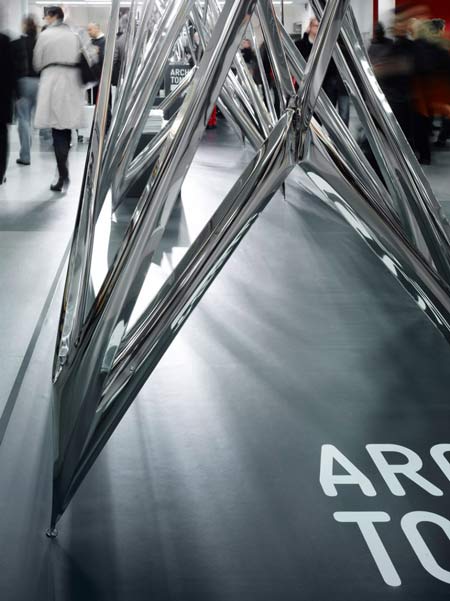
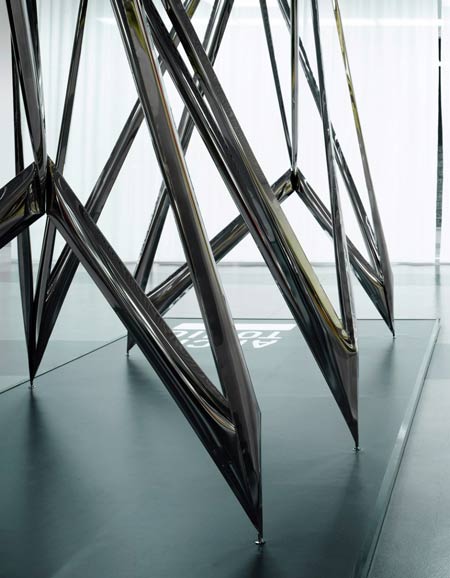
Cologne 2010: Polish designer Oskar Zieta of Zieta Prozessdesign created an installation of inflated stainless steel for online design products showcase Architonic at imm cologne earlier this month.

Called Architonic Concept Space III, the installation is made using FIDU technology, whereby welded sheet metal sleeves are pressure-inflated "like rubber toys" to create 3D forms.

Zieta also used FIDU to create his Plopp Stool.

See also our story from January 2008 about the Architonic Lounge by Tobias Wallisser and Chris Bosse. More about the project on Architonic's website here and here.

Photos are by gee-ly.
Here's some text from Zieta about the project followed by an explanation of the FIDU process:
--
Architonic Concept Space III on IMM Cologne
The Architonic Pavilion has been designed and produced by Zieta Prozessdesign in FIDU technology. FIDU allows to:
- create unique and individualized forms and produce them cost-effectively;
- create light and efficient constructions;
- increase ecology and cost-efficiency of steel-objects production
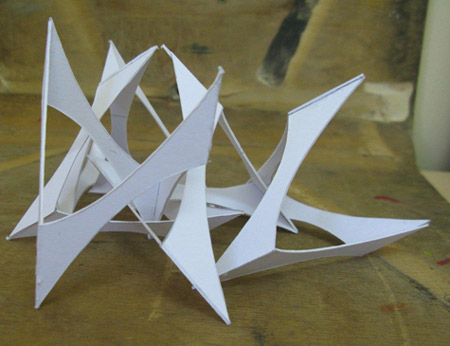
Zieta Prozessdesign develops FIDU technology and researches the possibilities of its application to the constructions of home objects, furniture, public elements and small architecture. Each of these fields is a new challenge in the forming process in FIDU technology. The development of new forms means experimenting with different shapes to develop the whole range of new systems and to constantly present more complex design objects in FIDU technology.
Zieta Prozessdesign combines 3 forces – research, design and production to bring the most complex solution and to eliminate any imperfections or inefficiencies on any stage of bringing concepts to life. Architonic Pavilion is a next step on a way to develop new applications of FIDU technology in light constructions.
About brief
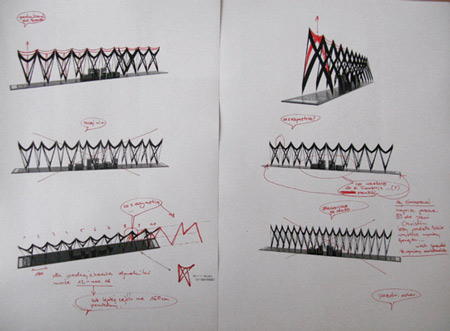
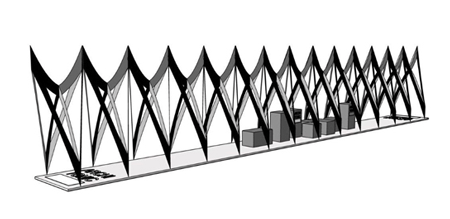
Design brief presented to us by Architonic and Messerli (logistics cooperating company) was very precise. It has precisely defined the modules of elements, the diversity of exhibition spaces and the assembly times. These parameters have defined our design line. Working on a concept, we began our experiments with a flat form of a rectangle. It has been deformed into a hyperbolic shape to bring a form of a tunnel. To increase stability and enhance the dynamic look of a form, the centre of a shape has been lowered. The final form has some characteristics of a form called hyperbole - a form which belongs to a group of a Non-Euclidean geometry. Basic research and analyses of these kinds of objects were undertaken in the beginning of XIX century by mathematicians: Janos Bolyai, Nikolai Ivanovitsch Lobatschevski and Carl Friedrich Gauss. Our basis to the conceptual work was a hyperbolic paraboloid.
About requirements
The elements of the Pavilion needed to fulfil many requirements. Installations like this have to be light and durable, easy to transport, easy to assembly and durable enough to maintain their quality during all the events, fairs and exhibitions. This is why we chose inox steel in its raw form – with no lacquer. The elements of the Pavilion have to fit to the dimensions limited by the exhibition spaces available during the festivals and design fairs.

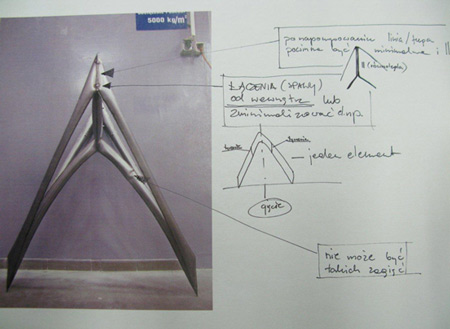
About joints and a final form
The aim was to design a stable, light and durable form with a load carrying capacity, taking advantage of the full potential of FIDU technology. To stabilize the conceptually-designed object, we had to prevent the movement in any axis in the joints. After experimenting with prototypes and a delicate re-conception we created elements which are called ‘the knots’. There are two kind of knots in every module - one on the inside of a module, formed by four bars, and one on the outside of module formed by three bars – a bar from an inside knot and two outside elements.

These joints stabilize an object in all possible directions and simultaneously create an interesting space composition. They give a full 3d possibility to FIDU technology, or at least show one of the methods to reach it. High glossiness of Inox gives an interesting effect of light and the reflections of each element. It is a combination of a strong and durable construction and attractive relations between all the elements. Each single element of a construction is configured to stabilize and influence the appearance of the whole structure. There is a ‘chaotic parameter’, which creates a visually-attractive installation. The task of a chaotic parameter is to perturb the repeated pattern of a structure.
Elements in each module can be positioned in different configuration and the inside knot can be re-positioned in x,y or z axis. This kind of experiments with a configuration gave a dynamic look to the structure. The pattern is still visible, but if the modules were put together in a different way, it would be gone. The most important step was to find the crucial relationships between single-elements, their joints, the modules and to set the final characteristics and positions of all the elements together and to create a highly-interesting visual effect of the whole structure.
About transport
One of the requirements known from the very beginning of the process was to make elements fit the standard cargo container. This requirement was fulfilled by enabling the modules to fit one another just like it is done with most of the common chairs. Putting one module into another gives high space-efficiency in transport and storage.
About packaging
Easy-to-scratch Inox surface needs to be handled with care and specially protected in transport. We used PE-foam of individually-calculated density, thickness and hardness – harder foam would scratch Inox, and softer would be less durable. The durability of the foam guarantees that it can be used many times.
FIDU MEANS INFLATING STEEL JUST LIKE RUBBER TOYS!
FIDU means inflating steel just like rubber toys!
With one exception – objects created this way are not necessarily toys.
Inflated steel sheets have a very high weight-capacity, so these funny looking shapes are indeed an innovative construction technology.
Developed as a method of steel sheet stabilization, FIDU opens new possibilities of forming for the design objects and ultra-light constructions.
IMAGINE THE SHAPE:
Every shape cut from steel sheet can be inflated into a 3d object.
The contours of the metal sheets are cut using a laser, welded together by a robot and then inflated at high pressure to form a 3d object.
HISTORY OF FIDU DEVELOPMENT BY OSKAR ZIETA AT THE DEPARTMENT OF CAAD AT ETH:
Oskar Zietaa has been working as a research associate and a teaching assistant at the chair of CAAD at the ETH in Zurich and writing his doctor thesis under supervision of Prof. Dr. Ludger Hovestadt.
Main focus of his thesis is the input of computer-controlled machines in processing of metal sheets in the architecture and design.
During his research at the ETH, Oskar Zieta has developed different methods of enhancing efficiency of technology for steel design, architecture and construction.
Among others, FIDU technology was developed. FIDU means that the two steel sheets, previously welded together around their edges, are inflated under high pressure to create a 3d object.
This method of 3d shaping means better efficiency and very high durability of products.