
Minimumhouse by Scheidt Kasprusch Architekten
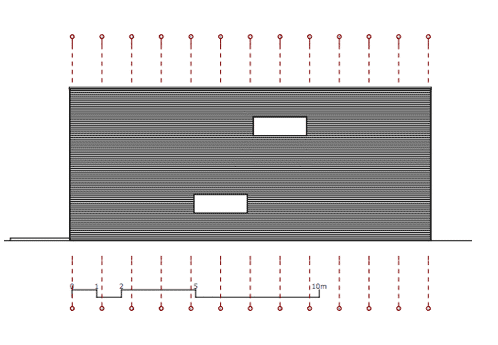
A chunky timber shell wraps over the north facade and roof of a woodland retreat near Berlin by German architects Scheidt Kasprusch.

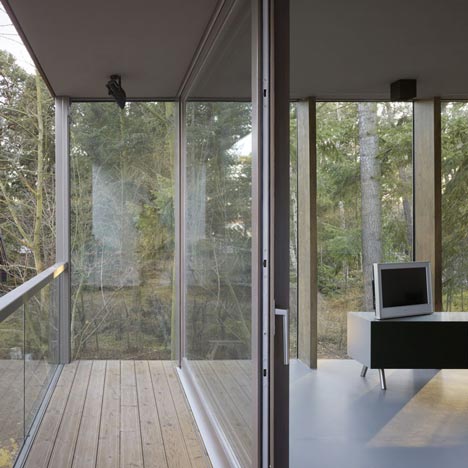
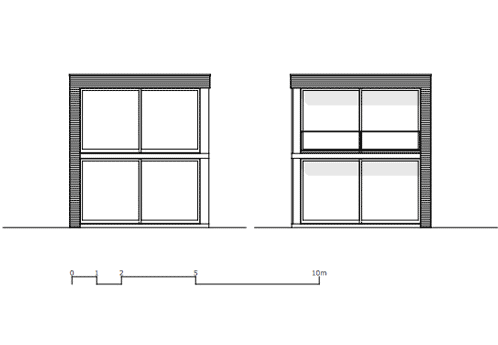
Completed in 2008, the two-storey house is fully glazed on the remaining three elevations.
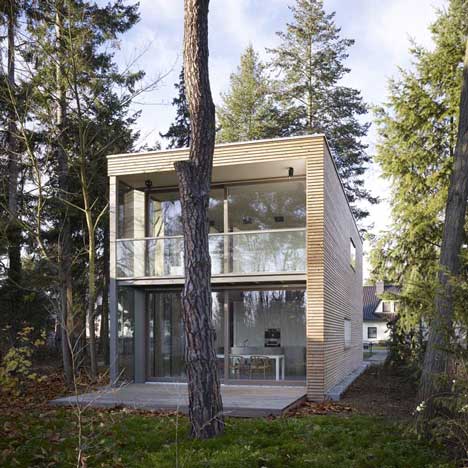

Timber mullions act as brise soleil to shade the south facade from direct sunlight.
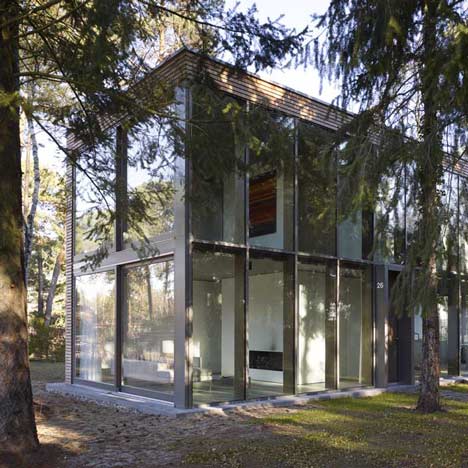

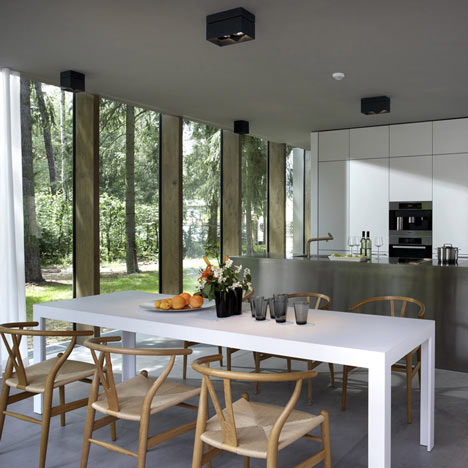
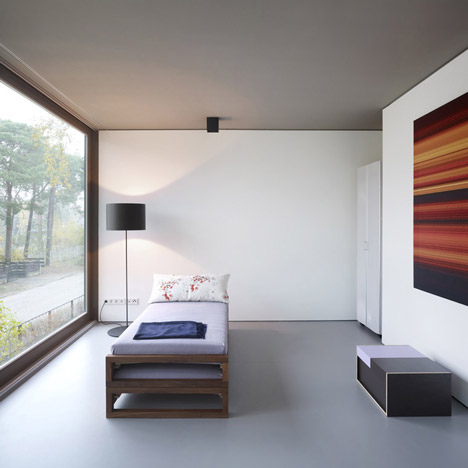
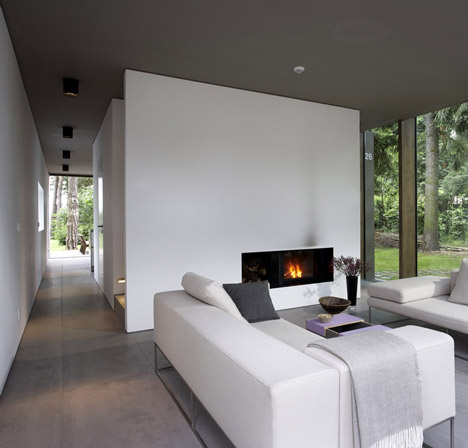
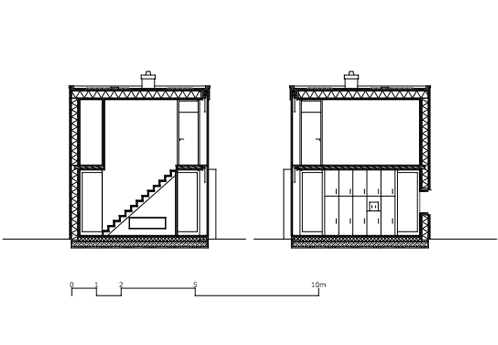
Inside the house, a staircase is located inside a central core that separates the living room from the dining room and divides the two first-floor bedrooms.
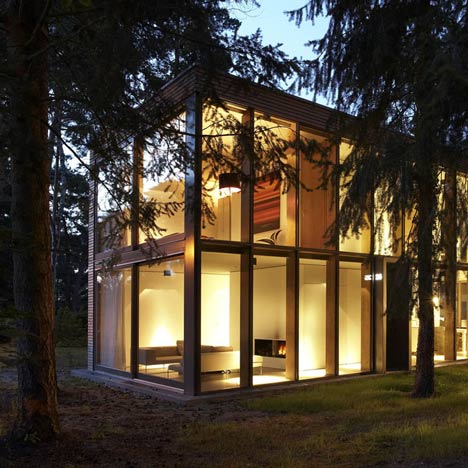

The dining room opens out to a decked terrace, while the master bedroom leads out to a balcony above.

This is the second project by Scheidt Kasprusch Architekten to be featured on Dezeen this week - see our earlier story about an archive clad in Corten.
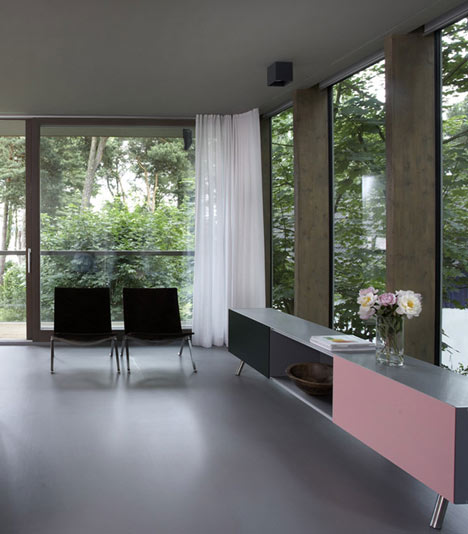

Photography is by Christian Gahl.

Here's some more text from Scheidt Kasprusch Architekten:
The minimumhouse at Mellensee, situated to the south of Berlin, is a prototype for a serial holiday and residentialhouse. Under the label minimumhouse it is offered including all furniture and fittings.

The concept was developed by the ideal of a house with maximum outdoor impressions and also by making full use of the solar yields for the building.

The reflections of glass and light make the three-side glassed building shells appear immaterial. The team consisting of architects, engineers, building physicists and executing companies developed a modular building concept, that allows a contemporary open-plan living with high ecological and economic standards.

The Institute for Building and Solar Technology, Braunschweig developed in several simulations various thermic and technical alternatives for the building services to obtain the optimal solution for each location.
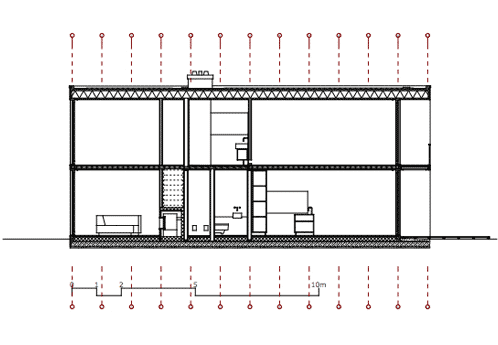
The annual heating requirements answer to the low-energy standard. Soil sensor, ceiling-mounted radiation heating, controlled ventilation and a heat recovery support thermic automation. A bus system constantly supervises and regulates the house.
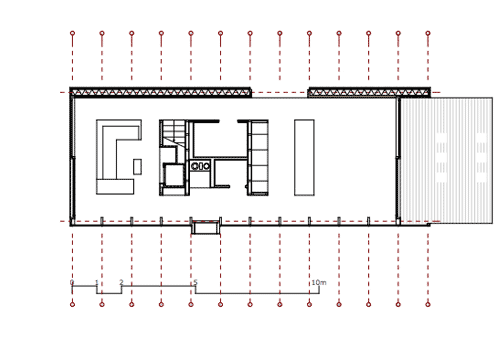
The floor plan organisation and the ideal orientation of the house –north side closed, the other sides paned- enable active and passive use of solar energy. A solar system is placed on the extensively vegetated flat roof.
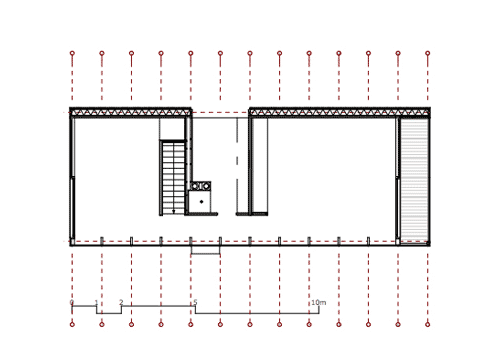
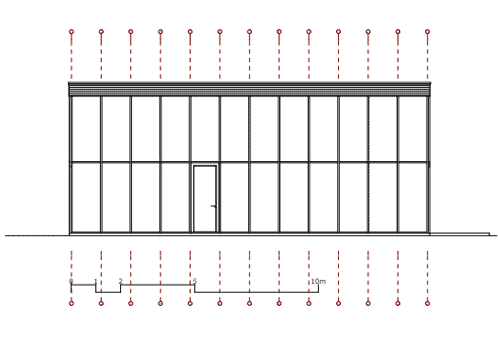
The northern wall is a highly insulated, two-shell timber frame construction. The southern facade is a flush fixed glazing mullion-transom construction. Sliding windows permit to open the west and east facades.
A core, that is placed in this volume, integrates building services, closet and flight of stairs and also divides the ground plan into zones. All materials and surfaces used for the minimumhouse have been chosen in accordance to ecological and sustainable criteria.
Residential house at Mellensee. Systems building in glass and wood
Materials:
Northern facade: a highly insulated, two-shell timber frame construction
Southern facade: a flush fixed glazing mullion-transom construction
Concept and development: Scheidt Kasprusch Architekten
Completion: 2008
Living space: 128 sqm
Gross floor area: 151 sqm
Cubature: 514 cbm
Location: Klausdorf, Germany