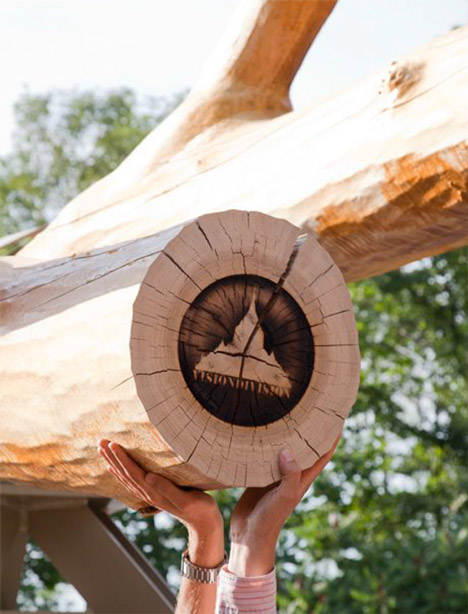
Chop Stick by Visiondivison
A 30-metre-long felled poplar tree protrudes either side of this kiosk by Swedish studio Visiondivision to support a row of playground swings at a country park in Indianapolis (+ slideshow).

The architects were commissioned by the Indianapolis Museum of Art to design a small kiosk for the surrounding 100 Acres park and they decided to create a structure that uses every part of a single felled tree.

"We investigated the different possibilities of harvesting something from Indiana and making it into a building," Visiondivision's Ulf Mejergren and Anders Berensson told Dezeen. "We really wanted to show where this building came from, take use of the raw materials' different properties and make it almost educational."

All the wood for the kiosk was strategically taken from the branches of the poplar tree. "Every board had to be calculated exactly and we had to point out where each board was coming from," said the architects.

The shingle cladding was made from the removed bark, which was flattened and dried in a kiln before reuse, while the leaves and flowers were pressed to make ornaments and even the syrup extracted from the bark was repackaged to be sold as snacks.

The remaining trunk was slotted through the walls to provide the structure for the swings and frame the outline of a picnic area.

Wooden trusses support the ceiling of the kiosk to ensure it is strong enough to support the weight of the tree and swings.

Summarising the project, the architects added: "We sometimes tend to forget where everyday things come from. Things doesn't just pop up from thin air. Everything has a history and this was a very important aspect of the project."

Another Visiondivison project that incorporates trees is The Patient Gardener, an hourglass-shaped hut Milan won’t be complete for 100 years. See more stories featuring trees »
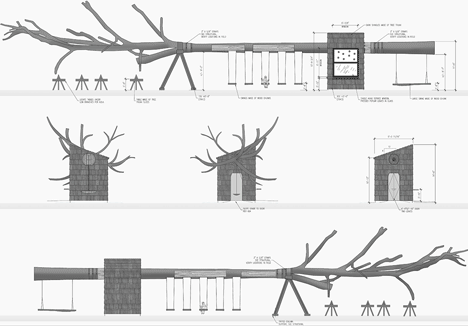
Above: elevations - click above for larger image
We also recently featured another set of playground swings, which generate enough power for their own lighting.
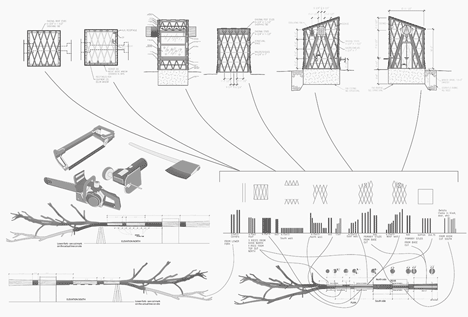
Above: kiosk construction diagram - click above for larger image
Photography is by Eric Lubrick (IMA), Donna Sink and Visiondivision.
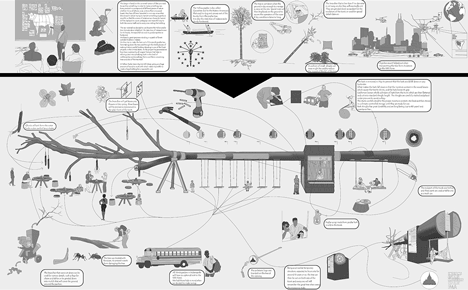
Above: concept diagram - click above for larger image
Here's a project description from the architects:
Visiondivision was commissioned by the Indianapolis Museum of Art to create an innovative concession stand for the 100 Acres: The Virginia B. Fairbanks Art & Nature Park.
The design is based on the universal notion that you need to sacrifice something in order to make something new. Every product is a compound of different pieces of nature, whether it is a cell phone, a car, a stone floor or a wood board; they have all been harvested in one way or another. Our project is about trying to harvest something as gently as possible so that the source of what we harvest is displayed in a pure, pedagogic and respectful way—respectful to both the source itself and to everyone visiting the building.
The raw material we selected is a 100-foot yellow poplar tree, the state tree of Indiana, known for its beauty, respectable size, and good properties as hardwood. We found a great specimen standing in a patch of forest outside of Anderson, Indiana. Our goal was to make the best out of this specific poplar tree, from taking it down and through the whole process of transforming it into a useful building that is now part of one of the finest art parks in the United States. As the project proceeded, we continued to be surprised by all of the marvelous features that where revealed in refining a tree into a building; both in the level of craftsmanship and knowledge of woodworkers and arborists, and also of the tree itself.
The tree was then transported to the park site, where it became the suspended horizontal beam of this new structure, which is almost entirely made out of the tree itself. The tree’s bark was removed to prevent it from falling on bystanders, a process that occurs naturally as the moisture content in the wood drops, causing the tree to shrink and the bark to lose its grip. Craftsmen loosen entire cylinders of bark from the trunk that are then flattened and cut into a standard shingle length. The shingles was carefully stacked and placed under pressure to avoid curling. The stacks was then kiln dried to the proper moisture content, sterilized, and kept in climate-controlled storage until they where ready for use. Bark shingles are very durable, long lasting (up to 80 years), and maintenance free.
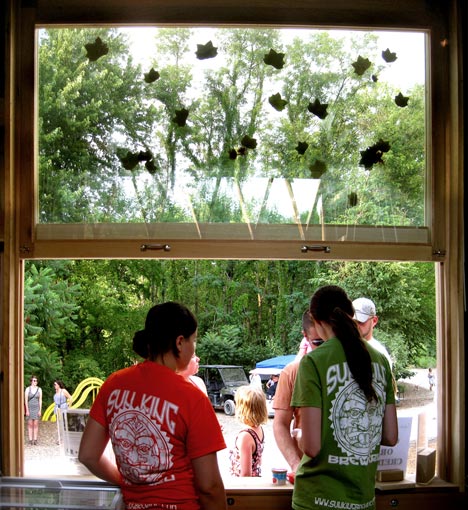
After debarking, pieces of wood are extracted from the suspended tree and used for each of the components of the concession stand; structural support of the construction, pillars and studs for the kiosk, swings under the tree for kids, chairs and tables to be placed under the tree’s crown, from which special fixtures made out of bark pieces will hang. Many school children visit 100 Acres, and we had those kids in mind when we decided to hang swings from the tree. On a smaller scale, we explored ways to use other parts of the tree in the concession stand, including pressed leaves and flowers that were taken from the tree and that became ornaments in the front glass of the kiosk.
We also made Yellow Poplar syrup that was extracted from the bark of the tree and that will be sold in the kiosk, thus meaning that you could actually eat a part of the building.
The delicate balance act of the risk of weakening the hovering tree with taking cuts from it versus having to have a certain amount of wood to stabilize and construct the kiosk and carrying the load from the tree itself was very challenging.
Many days was spent with the structural engineer trying different types of cuts in a computer model to optimize the structure. To be able to fit all pieces that needed to be taken from the tree into the actual cuts we needed to make drawings for every single piece taken from the tree. We also needed to optimize the kiosk both in size and in its constructions since it would take a lot of weight from the hovering trunk. The kiosk got a truss frame construction with two larger pieces of wood that are right under the tree. Using the schematics from our engineers force diagram program, we concluded that the wall closer to the end of the tree was taking more load, thus we sized up the two larger pieces of wood in that specific wall. All these alterations really just made the project more beautiful since the design became more refined in terms of more balanced proportions.
Architects: visiondivision through Anders Berensson & Ulf Mejergren
Local architect: Donna Sink
Client: Indianapolis Museum of Arts
Location: 100 Acres: The Virginia B. Fairbanks Art & Nature Park at The Indianapolis Museum of Arts. Indianapolis, IN, USA
Curators: Lisa Freiman & Sarah Green
Structural engineer: Dave Steiner
Contractor: The Hagerman group
Logger: Dave and Dave