University of Michigan explores low-carbon construction with robot-built pavilion
A team of students and researchers has shown how, with the help of robots, it's possible to build an intricate pavilion using only small pieces of timber.
The Robotically Fabricated Structure is the result of a project by the Adel Design Research (ADR) Laboratory at the University of Michigan's Taubman College of Architecture and Urban Planning.
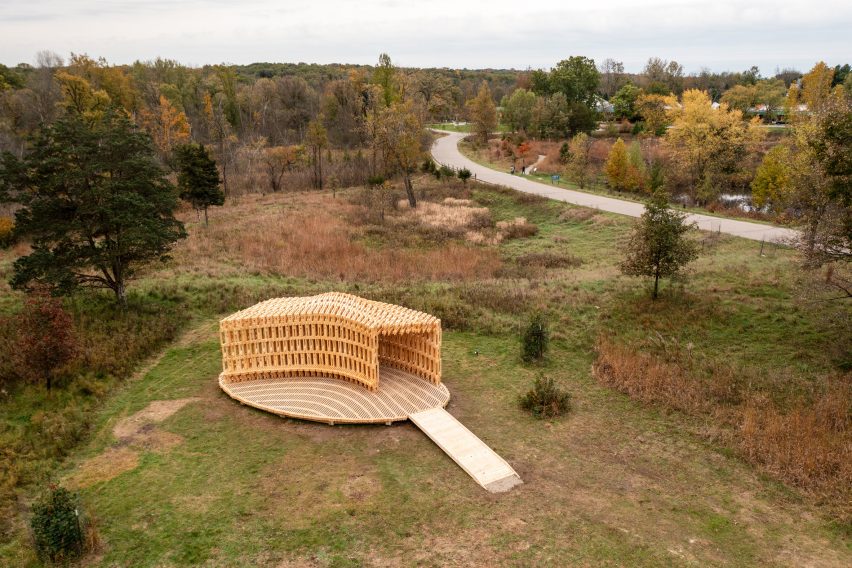

The ambition was to promote low-carbon construction, by showing it's possible to create complex architectural structures using wood that is sourced from the local region rather than imported.
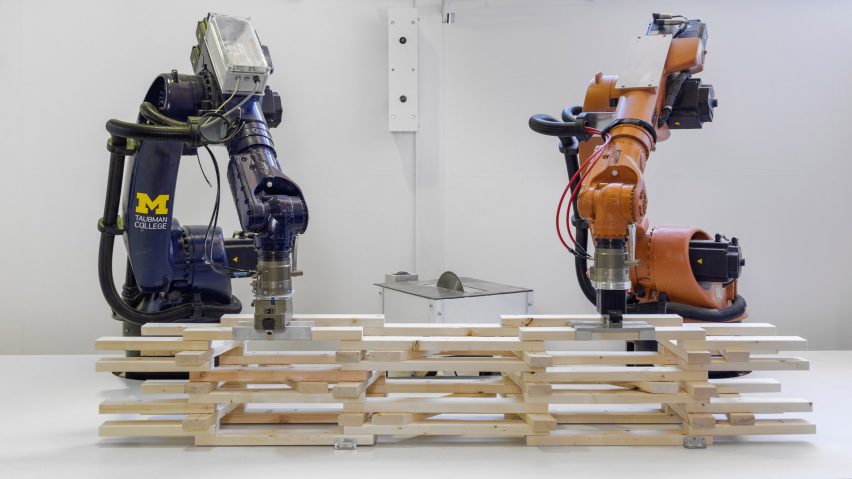
Custom algorithms were used to calculate the optimal arrangement for the timber 2x4s, removing the need for any larger beams within the structure.
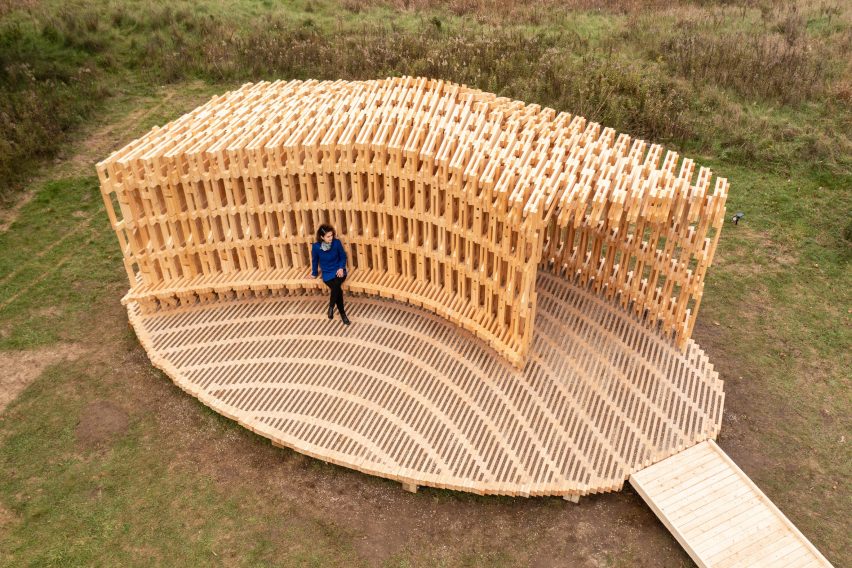

Robots assembled the components into a series of prefabricated frames, which were then delivered to site and slotted together by hand.
"The coupling of custom algorithms and robotic fabrication enables the feasible realisation of bespoke building components that are otherwise difficult or costly to achieve through conventional means and methods, with minimal construction waste," explained ADR, which is led by professor Arash Adel.
"Short elements enable the use of indigenous trees that cannot easily produce full-length building elements, construction and manufacturing off-cuts, and lumber elements reclaimed from the deconstruction of buildings, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable practice," said the team.
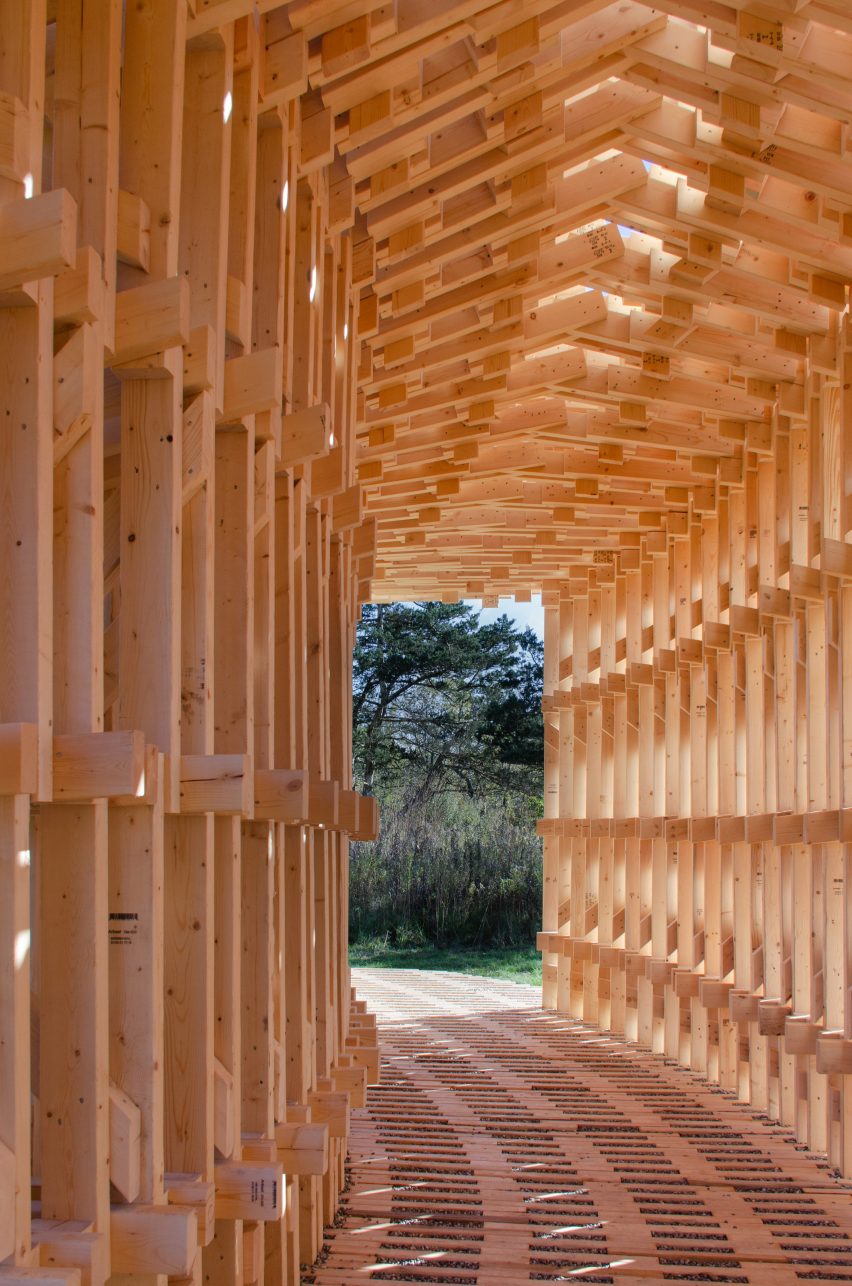

Robotically Fabricated Structure has been installed in the Matthaei Botanical Gardens in Ann Arbor, where it can be used as a place of rest and shelter, or host exhibitions and performances.
Raised on an oval-shaped timber platform, it takes the form of a curved tunnel with an integrated bench seat wrapping on of its edges.
The tunnel is made up of 20 robotically fabricated frames, which themselves are made up of various components. Each one is slightly different, which gives the structure its undulating shape.
As each piece of wood has the same thickness, it was possible to design these frames so that they slot together. This helped to reduce the need for screw fixings.
The design is longlisted for Dezeen Awards 2022 in the small building category.
The designers hope it can serve as an example of how robotic construction can enable more sustainable forms of construction and minimise waste.
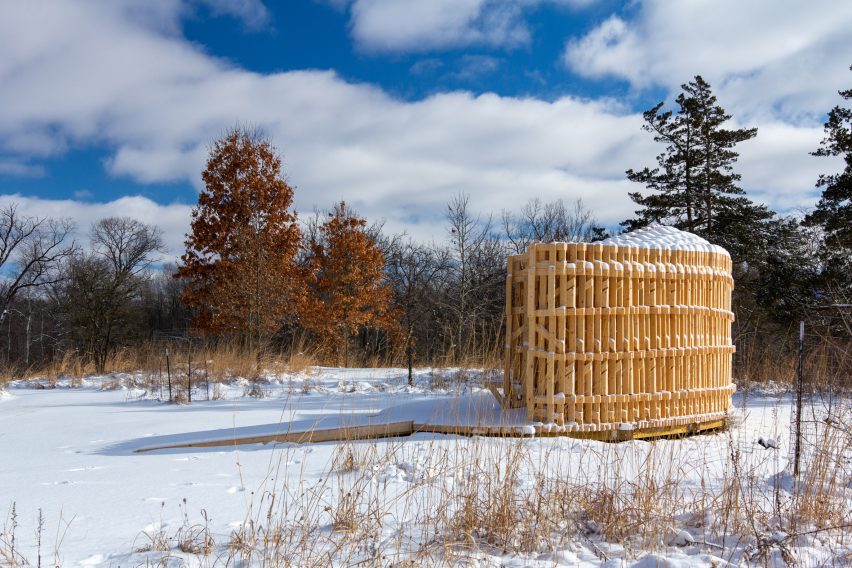

The wood is deliberately left untreated, to ensure it doesn't pollute its surroundings and can be easily disposed of at the end of its life.
"The integrated digital design and construction process for Robotically Fabricated Structure is a novel approach to reconsidering issues of material use, labour and the environment, to create intelligent and resourceful architecture with striking expressive qualities," said the designers.
The photography and video are by ADR Laboratory.
Project credits
Project lead: Arash Adel, ADR Laboratory
Research, design and fabrication assistants: Ben Lawson, Ryan Craney, Sarah Nail, Gabrielle Clune, Andrew Hoover, Juliette Zidek
Construction assistants: Abdallah Kamhawi, Tharanesh Varadharajan, Ali Fahmy, Elliot Smithberger, Qian Li, Nadim Hajj Ahmad, Joshua Powell, Ivan Gort-Cabeza de Vaca
Students: Ruxin Xie, Daniel Ruan, Xinran Li, Jingwen Song, Mehdi Shirvani, Mackenzie Bruce, Chris Humphrey
Structural engineers: Robert Silman Associates Structural Engineers
Sponsor: Herbert W and Susan L Johe Fund, Taubman College of Architecture and Urban Planning, University of Michigan
Supporters: Jonathan Massey, McLain Clutter, Catie Newell, Wes McGee, Cynthia Radecki, Earl Bell