Perot Museum of Nature and Science by Morphosis
American firm Morphosis has completed a museum of nature and science in Dallas where visitors begin their tour by taking an escalator journey to the uppermost floor.
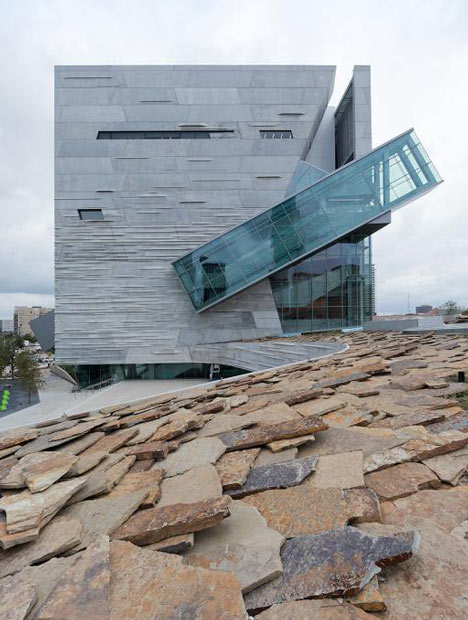

Surrounded by glazing, the escalator streaks diagonally across the striated concrete facade then angles back inside the building. At the top, each visitor is faced with a view of the city before spiralling their way back down through five exhibition floors into the atrium where they first arrived.

The Perot Museum of Nature and Science is sited in Victory Park, downtown Dallas, and when it opens to the public next weekend it will replace some of the facilities of the existing Museum of Science and Nature, located further east in Fair Park.

Morphosis' founder Thom Mayne conceived the building as a large cube emerging from a series of landscaped lower tiers. These levels, designed in collaboration with landscape architects Talley Associates, are covered in stones and drought-resistant grasses that are typical of the landscape in Texas.

A 3D cinema, auditorium, cafe and shop accompany the eleven exhibition galleries inside the building.
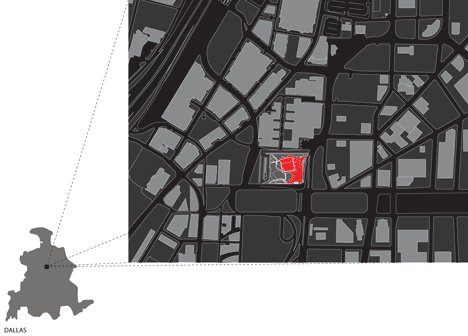
Above: site plan - click above for larger image
"The Perot Museum of Nature and Science is a gift to the city of Dallas," said Mayne. "It is a fundamentally public building – a building that opens up, belongs to and activates the city. It is a place of exchange. It contains knowledge, preserves information and transmits ideas; ultimately, the public is as integral to the museum as the museum is to the city."
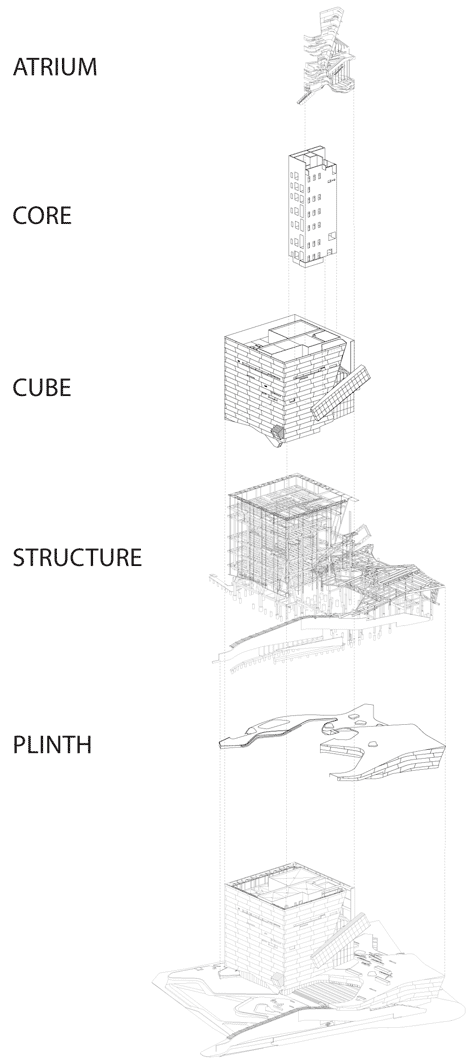
Above: exploded axonometric diagram - click above for larger image
See more projects by Morphosis on Dezeen, including a floating house for Brad Pitt’s Make It Right Foundation in New Orleans.
Photography is by Iwan Baan.
Here's a project description from Morphosis:
Museums, armatures for collective societal experience and cultural expression, present new ways of interpreting the world. They contain knowledge, preserve information and transmit ideas; they stimulate curiosity, raise awareness and create opportunities for exchange. As instruments of education and social change, museums have the potential to shape our understanding of ourselves and the world in which we live.
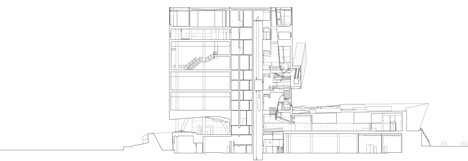
Above: east-facing section - click above for larger image
As our global environment faces ever more critical challenges, a broader understanding of the interdependence of natural systems is becoming more essential to our survival and evolution. Museums dedicated to nature and science play a key role in expanding our understanding of these complex systems.
The new Perot Museum of Nature and Science in Victory Park creates a distinct identity for the Museum, enhances the institution’s prominence in Dallas and enriches the city’s evolving cultural fabric. Designed to engage a broad audience, invigorate young minds, and inspire wonder and curiosity in the daily lives of its visitors, the Museum cultivates a memorable experience that persists in the minds of its visitors and that ultimately broadens individuals’ and society’s understanding of nature and science.
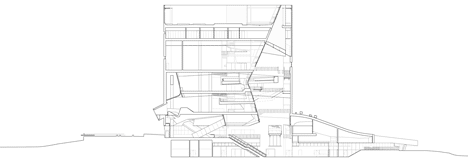
Above: north-facing section one - click above for larger image
The museum strives to achieve the highest standards of sustainability possible for a building of its type. High performance design and incorporation of state of the art technologies yields a new building that minimizes its impact on the environment.
This world class facility inspires awareness of science through an immersive and interactive environment that actively engages visitors. Rejecting the notion of museum architecture as neutral background for exhibits, the new building itself is an active tool for science education. By integrating architecture, nature, and technology, the building demonstrates scientific principles and stimulates curiosity in our natural surroundings.
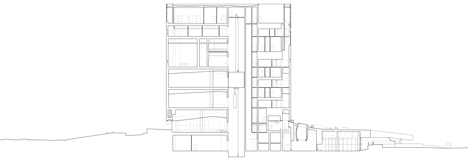
Above: north-facing section two - click above for larger image
The immersive experience of nature within the city begins with the visitor’s approach to the museum, which leads through two native Texas ecologies: a forest of large native canopy trees and a terrace of native desert xeriscaping. The xeriscaped terrace gently slopes up to connect with the museum’s iconic stone roof. The overall building mass is conceived as a large cube floating over the site's landscaped plinth. An acre of undulating roofscape comprised of rock and native drought-resistant grasses reflects Dallas’s indigenous geology and demonstrates a living system that will evolve naturally over time.
The intersection of these two ecologies defines the main entry plaza, a gathering and event area for visitors and an outdoor public space for the city of Dallas. From the plaza, the landscaped roof lifts up to draw visitors through a compressed space into the more expansive entry lobby. The topography of the lobby’s undulating ceiling reflects the dynamism of the exterior landscape surface, blurring the distinction between inside and outside, and connecting the natural with the manmade.
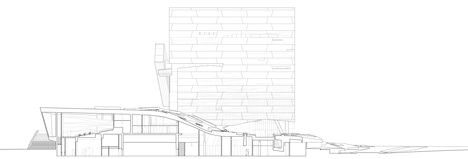
Above: west-facing section one - click above for larger image
Moving from the compressed space of the entry, a visitor’s gaze is drawn upward through the soaring open volume of the sky-lit atrium, the building’s primary light-filled circulation space, which houses the building’s stairs, escalators and elevators. From the ground floor, a series of escalators bring patrons though the atrium to the uppermost level of the museum. Patrons arrive at a fully glazed balcony high above the city, with a bird’s eye view of downtown Dallas. From this sky balcony, visitors proceed downward in a clockwise spiral path through the galleries. This dynamic spatial procession creates a visceral experience that engages visitors and establishes an immediate connection to the immersive architectural and natural environment of the museum.
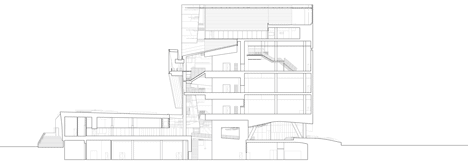
Above: west facing section two - click above for larger image
The path descending from the top floor through the museum’s galleries weaves in and out of the building’s main circulation atrium, alternately connecting the visitor with the internal world of the museum and with the external life of the city beyond. The visitor becomes part of the architecture, as the eastern facing corner of the building opens up towards downtown Dallas to reveal the activity within. The museum, is thus, a fundamentally public building – a building that opens up, belongs to and activates the city; ultimately, the public is as integral to the museum as the museum is to the city.